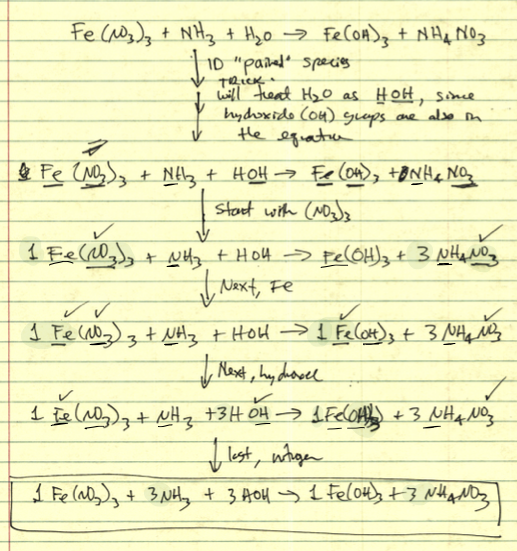Blog: BCE (Balancing Chemical Equations)

Sig Fig blog
Page Index:
Introduction
The mechanics of BCE problems can range from simple (can be worked just by looking) to very complex (requires multiple algebraic equations). Most are of intermediate difficulty: they either require no algebra, or they require only one simple algebraic equation to determine the coefficient of some last remaining reactant/product.
A second factor affecting problem difficulty is the amount of information given within the question itself. These tend to fall into one of three general levels:
- An unbalance equation with both reactants and products is provided.
(BCE process) - Only reactants are provided. The problem requires that the correct products be determined before the BCE process can begin.
(Product identification + BCE process) - Only the names of reactants are given. A working knowledge of nomenclature rules is necessary to identifying the starting materials.
(Nomenclature + Product identification + BCE process)
Learn How to Balance Chemical Equations: Video Series
A series of five videos explain the BCE process in detail, with examples. Those videos are located in the CHEM 1305 Exam 2 playlist, of the DrStephensonChemistry youtube channel.
See videos 6.01–6.05:
- 6.01 Introduction to Chemical Equations
- 6.02 Balancing Chemical Equations (Part 1): Introduction
- 6.03 Balancing Chemical Equations (Part 2): Twin Elements Method Illustrated
- 6.04 Balancing Chemical Equations (Part 3): Cross-multiplication and Fractionation
- 6.05 Balancing Chemical Equations (Part 4): Sample Problems
Miscellaneous Sample Problems
Question 1: "Pair → Charge Neutral → BCE" Sequence Problem
A Level-3 problem.
- ① Recognize the problem as an acid base
② PAIR the cation of each reactant with the anion of the other (i.e., double displacement)
③ Make each pair CHARGE NEUTRAL by adjusting subscripts
④ Balance the chemical equation (BCE) by adjusting coefficients -

Question 2: BCE Example (video): chromium metal + sulfuric acid
-
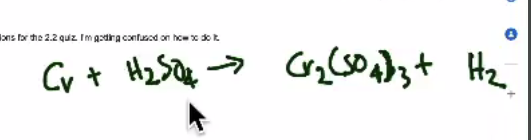
- This video is the result of a former student BCE query.
- CLICK HERE for video